🧩 Integration Design Patterns
Each Design Pattern reflects a common use case in our environment, with a tailored approach depending on the nature, frequency, and criticality of the data flow.
To ensure clarity, scalability, and reusability across our data ecosystem, we have structured our integration approach into three architectural domains, each aligned with specific types of use cases:
🔧 Service Oriented : For synchronous or asynchronous API interactions, where services are directly invoked to retrieve or trigger data.
📣 Event Driven : For real-time or decoupled communication based on events, enabling reactive and scalable data flows.
🧮 Data Driven : For batch or incremental data synchronization, where data itself is the trigger for movement or transformation.
Each scenario below illustrates a concrete example of how these patterns are applied in our industrial context.
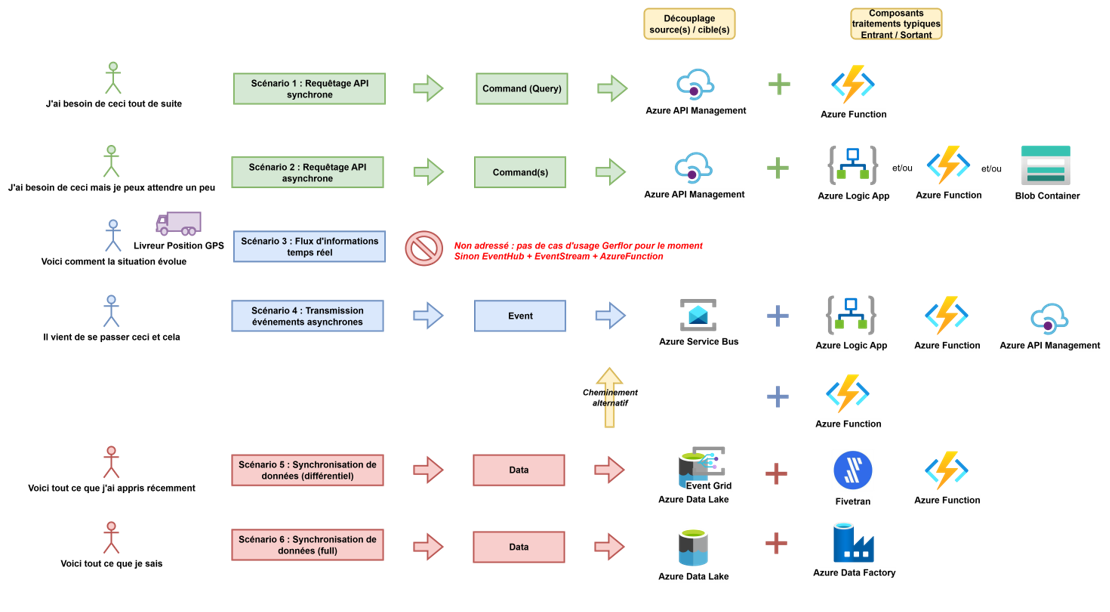
🗺️ Overview
🧠 Why These Patterns?
- ✅ Standardization of integration practices
- 🔄 Reusability of components
- 🧩 Adaptability to various business use cases
- 🔒 Robustness and resilience of data flows
⚡ Synchronous API Request
Domain: Service Oriented
A direct API call with an immediate response. Used for simple and fast integrations with real-time needs.
Example
An internal application queries an API in real time to retrieve live pricing for an item.
📨 Asynchronous API Request
Domain: Service Oriented
The API call triggers a long-running or delayed process. The response is retrieved later via polling or a message bus.
Example
A request is sent to generate a production report. Once ready, the report is retrieved via polling or a message on Azure Service Bus.
📡 Real-Time Information Flow
Domain: Event Driven
Events are emitted and processed in real time using Kafka streams. Ideal for high-frequency or critical data.
Example
Real-time monitoring of temperature and humidity sensors in factories to automatically adjust production parameters.
📬 Asynchronous Event Transmission
Domain: Event Driven
Events are published to a topic and consumed by one or more subscribers. Enables strong decoupling between producers and consumers.
Example
When a purchase order is validated in the ERP, an event is emitted to trigger stock updates, logistics planning, and invoicing.
🧮 Differential Data Synchronization
Domain: Data Driven
Regular data synchronization using change data capture (CDC). Optimized for large volumes.
Example
Daily synchronization of sales data from Salesforce to our Data Warehouse to feed Power BI dashboards.
📦 Full Data Synchronization
Domain: Data Driven
Full table or file loads at scheduled intervals. Used for low-volume sources or when CDC is not available.
Example
Weekly loading of Excel forecast files sent by subsidiaries into the Azure Data Lake.